Every individual has a right to privacy and to decide where and with whom the data should be shared.
Introducing the India Digital Personal Data Protection Act—a groundbreaking legislative milestone designed to safeguard the rights and privacy of individuals across the nation. This comprehensive legislation establishes a robust framework governing the entire lifecycle of personally identifiable information (PII), encompassing its collection, utilization, storage, and transfer.
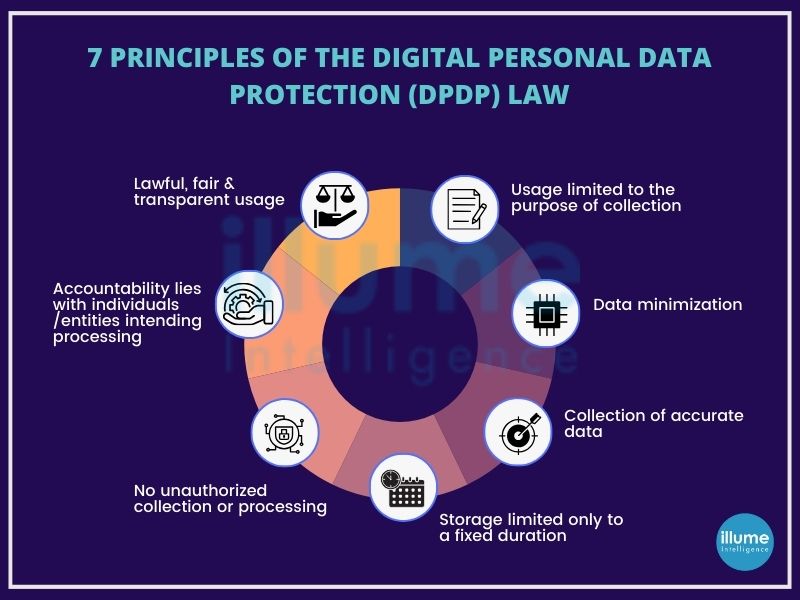
In navigating the dynamic landscape of digital data, a thorough grasp of the fundamentals of this act becomes indispensable. Compliance is not just a requirement but a commitment to upholding the principles that form the backbone of this progressive legislation. Stay informed, stay compliant, and embrace the future of responsible data management under the India Digital Personal Data Protection Act.
At the forefront of data protection in the digital age stands the DPDP Act, a pivotal legislation with the singular mission of safeguarding the personal data of individuals while empowering them with unprecedented control over their information. In an era marked by the incessant collection, processing, and sharing of personal data, this act emerges as a beacon, establishing a robust legal framework that addresses the myriad concerns and risks inherent in such activities.
Applying to a broad spectrum of entities, including government agencies, private enterprises, and organizations dealing with personal data, the DPDP Act casts a wide net to ensure comprehensive accountability. Its jurisdiction spans entities collecting, processing, storing, or transmitting personal data within India or from individuals within the country. By doing so, the act mandates compliance with its regulations, placing all stakeholders under the umbrella of responsibility.
Who complies with the DPDP?
The expansive reach of the Bill encompasses your organisation, necessitating compliance if:
-
Your organisation engages in the processing of Personal Data belonging to individuals.
-
Personal Data is processed within the geographical bounds of India by your organisation.
-
The Personal Data collected by your organisation originates from online sources.
-
In the case of offline data collection, if the acquired information is subsequently digitized.
-
Your organisation engages in the processing of Personal Data outside the borders of India, specifically linked to profiling or activities related to offering goods or services to Data Principals within the territory of India.
In aligning with these criteria, your company falls within the ambit of the Bill, emphasizing the importance of ensuring adherence to the stipulated regulations for comprehensive data protection and compliance.
Why Do Businesses Need To Comply With The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Law?
Businesses are required to adhere to the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Law for a multitude of compelling reasons:
-
Data Privacy Protection: Compliance is synonymous with safeguarding individuals' data, offering a robust shield against unauthorized access, misuse, and data breaches. By prioritizing data privacy, businesses instil confidence in their customers, building a foundation of trust that is pivotal in today's digital landscape.
-
Legal Obligation: The DPDP Law establishes a mandatory framework for organizations handling personal data. Compliance isn't just a best practice; it's a legal imperative. Businesses that fall in line with the stipulations of the law mitigate the risk of legal actions, ensuring that their operations align with the regulatory landscape.
-
Business Reputation: Non-compliance poses a significant threat to an organization's reputation. In an era where trust is paramount, failing to meet the standards set by the DPDP Law can erode customer trust and damage an organisation's standing in the market. A tarnished reputation can result in losing existing customers and hamper acquiring new business opportunities.
-
Avoiding Fines and Penalties: The DPDP Law doesn't just set guidelines; it wields substantial consequences for non-compliance. Organizations that fail to meet the prescribed standards risk facing hefty fines, with penalties extending up to 250 crores. The financial impact of such fines can be severe, affecting the organization's financial health and potentially jeopardizing its business continuity.
In essence, compliance with the DPDP Law is not merely a regulatory formality; it is a strategic imperative for businesses seeking to thrive in the digital era while upholding the principles of data protection, legal responsibility, and maintaining a positive brand image.
How Can Businesses Comply With The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Law?
Achieving compliance with the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Law necessitates a strategic and proactive approach. Here are key steps that businesses should take to align with the regulatory framework:
-
Data Identification:
Thoroughly identify and document all personal data that the business collects and processes. This includes data obtained online, offline, or through any other channels.
-
Consent Management:
Implement robust consent mechanisms to ensure that individuals explicitly agree to the collection and processing of their data. Communicate the purpose for which the data is being collected and seek consent accordingly.
-
Data Security Measures:
Institute stringent security measures to safeguard personal data from unauthorized access, breaches, or misuse. Employ encryption, access controls, and other security protocols to create a robust defense against potential threats.
-
Data Retention Policies:
Develop and adhere to data retention policies to ensure that personal data is retained only for as long as necessary. Regularly assess the need for data storage and promptly delete information that is no longer required.
-
Individual Rights Response:
Establish a streamlined process to respond to individual requests about their data. This includes providing access to the data, correcting inaccuracies, or erasing the data when requested. Ensure that this process is transparent, efficient, and aligns with regulatory requirements.
-
Privacy by Design:
Integrate privacy considerations into the design and development of products, services, and systems from the outset. This proactive approach, known as Privacy by Design, ensures that data protection is embedded into the core of the business processes.
-
Employee Training:
Conduct regular training sessions to educate employees on the importance of data protection and compliance with the DPDP Law. Ensure that all staff members are well-informed about their responsibilities in handling personal data.
-
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs):
Conduct DPIAs to assess the impact of data processing activities on individual privacy. This helps in identifying and mitigating potential risks and ensures that privacy considerations are integral to business decisions.
-
Data Breach Response Plan:
Develop a comprehensive plan for responding to data breaches. This should include immediate steps to contain the breach, notifying relevant authorities, and communicating with affected individuals as required by the DPDP Law.
By diligently implementing these steps, businesses can not only navigate the complexities of the DPDP Law but also foster a culture of responsible data management, thereby building trust with customers and maintaining compliance with regulatory standards.